• 4:44 PM, 3.10.07
RESPIRATIONNNNNNNNNNNN DAMNJOOOOO.WTF is respiration?
-oxidation of food to release energy in LIVING cells.
WHY do living organisms respire?
-cause they noob. okay kidding, they need to get energy to maintain itself to move, excrete, grow and reproduce.
WHO respires?
-small organisms, unicelluar stuff.
-large organisms like fish.
-humans.
-plants.
HOW do organisms obtain enough oxygen for aerobic respiration?
-through gaseous exchange.
-between organism and environment.
-occurs in lungs.
-includes breathing. (muscular contractions and movement of the ribs)
Aerobic Respiration is?
-breakdown of food using oxygen.
~large amount of energy is released.
-waste products = CO2 and H2O.
GLUCOSE + OXYGEN -> CARBON DIOXIDE + WATER + LARGE AMOUNT OF ENERGY.
-occurs in mitochondria.
-many reactions involved.
-animals and green plants respire aerobically.
Then whatto about Anaerobic Respiration?
-breakdown of food with NO oxygen.
~small amount of energy released.
GLUCOSE -> CARBON DIOXIDE + ETHANOL (FERMENTATION) + SMALL AMOUNT OF ENERGY.
-less energy yield.
-occurs in microorganisms, yeast.
-glucose molecules partially broken down.
-ethanol still converts energy.
in muscles,
-muscles cells carry out aerobic respiration first.
-people take in more oxygen.
-heart beats faster to bring more oxygen to muscles.
-muscle cells carry out anaerobic respiration to produce extra energy.
GLUCOSE-> LACTIC ACID + SMALL AMOUNT OF ENERGY.
-lactic acid builds up. (oxygen debt)
-lactic acid removed from muscles and transported to liver.
-some oxidized to produce energy, remaining all converted to glucose.
in yeast,
-respire anaerobically without oxygen. (alcoholic fermentation)
-releases ethanol and carbon dioxide.
-makes wines and beers.
-used in baking as leavening agent.
Some uses of energy;
-synthesis of proteins from amino acids.
-building up of protoplasm for growth.
-cell division.
-heartbeat.
-respiratory movements and other muscular contractions.
-active transport.
-transmission of nervous impulses.
-heat released during respiration is needed to keep us warm.
Tissue respiration;
-oxidation of organic food molecules.
-gives out energy, carbon dioxide and water.
-occurs within living cells.
Gaseous exchange in animals;
-unicellar.
~large SA:V ratio.
~diffusion through cell membrane. (mode of gaseous exchange)
-large organisms.
~small SA:V ratio.
~thickened external surface.
~breathe through special organs (ie. gills for fish.)
~special breathing movements as well.
Breathing Mechanisms;
-consists of 2 phases.
~taking in of air. (inspiration)
~giving out of air. (expiration)
Gaseous exhange in green plants;
-simple diffusion.
-layer of waterproof cork tissue develops beneat the epidermis in old woody stem.
-opening (lenticels) are formed in cork layer for gaseous exhange.
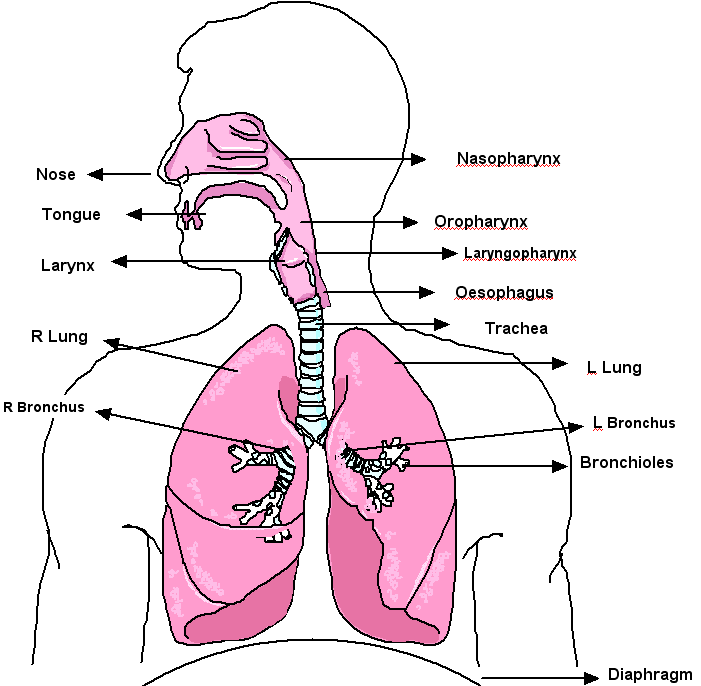 respiration system! nice picture. >D
respiration system! nice picture. >DPathway of air molecules;
-external nostrils lead into two nasal passages lined with moist mucous membrane.
-advantages of breathing through nose.
~dust and foreign particles are trapped by hairs in nostrils and mucus.
~air is warmed and moistened before entering lungs.
~harmful chemicals are detected by small sensory cells.
-air enters the pharynx and into the larynx before entering the trachea through the glottis.
Features of air passages;
-trachea and bronchi lined by epithelium bearing cillia.
-gland cells secrete mucus to trap dust particles and bacteria.
-cillia sweep particles. (swallowed into oesophagus)
Adaptations of alveoli for efficient gaseous exchange;
-large SA.
-one cell thick (faster rate of diffusion)
-thin film of moisture covering surface. (allows oxygen to dissolve)
-walls are richly supplied with blood capillaries. (flow of blood maintains concentration of gases)
Intercostal muscles;
-external and internal intercostal muscles are found between ribs.
-antagonistic. (explained what's that in the digestive part. :S)
Inspiration;
-diaphragm contracts and flattens.
-external intercostal muscles contract while internal intercostal muscles relax.
-ribs and sternum move upwards and outwards.
-air pressure in lungs causes expansion to fill up thorax.
-air pressure inside lungs decrease.
-atmospheric pressure is now higher.
-air rushes into lungs.
Expiration;
-diaphragm relaxes and arches upwards.
-external intercostal muscles relax while internal intercostal muscles contract.
-ribs and sternum move downwards and inwards.
-volume of thorax decreases.
-lungs are compressed and air pressure inside increases as volume decreases.
-atmospheric pressure lower.
-air is forced out to exterior.
Diaphragm;
-dome-shaped muscle separating thorax from abdomen.
-helps vary volume of thorax.
Thorax;
-supported by ribs.
-which are attached dorsally to backbone and can move up or down.
-ribs attached ventrally to chest bone.
Lungs;
-lined by two transparent elastic membranes called the pleura.
-lubricating fluid allows membranes to slide over each other easily during breathing.
Bronchi;
-trachea divides into two bronchi.
-each bronchus ends in bronchioles which end in air sacs or alveoli.
Trachea;
-lies in front of oesophagus.
-extends from larynx into chest.
-supported by C-shaped rings of cartilage.
Gaseous exchange in alveoli;
-by diffusion.
-concenration gradient between blood and alveolar air.
-gradient maintained by,
~continuous flow of blood through capillaries.
~breathing air in and out of the alveoli.
-alveolar air --oxygen--> blood capillaries.
-alveolar air <-carbon dioxide-- blood capillaries. -one cell thick membrane separating capillaries from alveolar air is permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide. -alveolar air contains higher concenration of oxygen. -oxygen dissolves in moisture lining alveolar walls and then diffuses into capillaries. Vital Capacity = tidal air + complemental air +supplement air.
What is the stimulus for breathing?
-high concentration of CO2 in the blood or alveolar air, not lack of oxygen.
Chronic bronchitis;
-long term.
-caused by irritant particles.
-signs include paralysed cilla, blocked airways, persistent coughing, inflamed epithelium, excessive mucus.
How oxygen is absorbed in lungs;
-oxygen combines with haemoglobin in the RBCs to form oxyhaemoglobin.
Removal of CO2 from body;
-tissue cells produce CO2. (catalysed by carbonic anhydrase to form carbonic acid in RBC)
-carbonic acid coverted into hydrogencarbonate ions which difuse out of RBC.
-in lungs, ions diffuse into RBC and are converted into carbonic acid, then water + CO2.
-diffuses out of capillaries into alveoli and expelled during exhalation.
Emphysema;
-caused by persistent and violent coughing.
-signs include broke partition walls between air sacs and difficulty in breathing.
-when a person has chronic bronchitis and emphysema, he suffers from chronic obstructive lung disease.
Comparison between respiration and photosynthesis;
-respiration;
~energy is liberated.
~oxygen is used and CO2+water given off.
~a catabolic (destructive) process.
~occurs at all times in all cells.
~results in a loss of dry mass.
-photosynthesis;
~energy is stored in carbohydrate molecule.
~CO2+water are used while oxygen is given off.
~anabolic (constructive) process.
~only occurs in cells containing chlorophyll and in the presence of sunlight.
~results in a gain of dry mass.
DONE WITH RESPIRATION YAY.